Entrepreneurial Processes, Distinctions, Educational Foundations
Table of Contents
Entrepreneurial Landscape: Understanding Processes, Distinctions, and Educational Foundations
Entrepreneurship plays a critical role in economic development and innovation. For students of entrepreneurship, especially those in the Philippines, gaining a deep understanding of the entrepreneurial process, differentiating entrepreneurial from managerial roles, and recognizing the value of entrepreneurial education is essential. This comprehensive discussion aims to provide a clear framework for aspiring entrepreneurs and equip them with the foundational knowledge to succeed in business.
1. The Entrepreneurial Process: From Idea to Growth
The entrepreneurial process is a structured sequence of steps that guide individuals from the initial conception of a business idea through launching and growing a sustainable enterprise. Mastering this process enhances clarity and decision-making, vital for turning vision into reality.
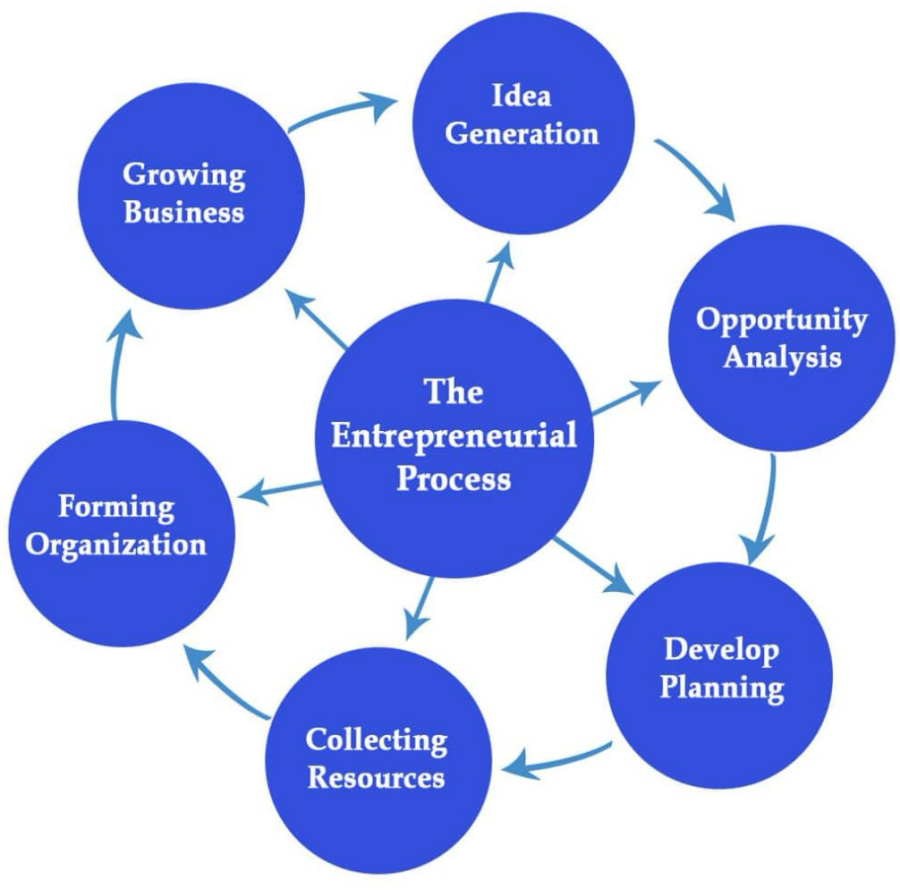
Key Stages of the Entrepreneurial Process
Idea Generation
This stage involves spotting a problem or need in the market and creating a potential solution or business idea. For example, many Filipino entrepreneurs identified the demand for affordable, eco-friendly packaging as a business opportunity due to increasing environmental awareness.
Opportunity Analysis
Once an idea is generated, it must be rigorously evaluated. This involves researching market demand, assessing competitors, estimating profitability, analyzing risks, and determining sustainability. In the Philippines, businesses like Salt & Pepper Foodie started by analyzing the increasing demand for local gourmet food experiences, helping them carve a niche.
Planning
Planning translates the opportunity into an actionable roadmap. Entrepreneurs develop detailed business plans outlining the value proposition, target market, marketing strategies, operational processes, financial projections, and risk mitigation approaches.
Collecting Resources
With a plan in place, entrepreneurs gather essential resources such as capital, skilled labor, technology, and materials. For example, Filipino start-ups may seek funding from sources like the Department of Trade and Industry’s (DTI) Small Business Corporation (SBC) or private investors.
Forming an Organization
This phase involves legalizing the business by registering it with appropriate government agencies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) or the Department of Trade and Industry (DTI), and setting up the organizational structure.
Growing the Business
After launching, the focus shifts to sustaining and expanding the business. This includes continuous monitoring of performance, adapting to market changes, optimizing operations, and exploring new growth opportunities. Local SMEs often leverage government programs like the Negosyo Centers for mentorship and scaling up their ventures.

2. Managerial versus Entrepreneurial Decision-Making
Understanding the distinction between entrepreneurial and managerial decision-making is key to navigating the business world effectively.
Entrepreneurial Decision-Making
Entrepreneurs prioritize innovation, creative problem-solving, and opportunity recognition. They often embrace uncertainty and take calculated risks on novel ideas, relying on intuition, flexibility, and a vision-driven mindset. For instance, a tech startup founder in Cebu might pursue emerging markets despite limited data, betting on future trends.
Managerial Decision-Making
Managers focus on maintaining operational efficiency, optimizing existing resources, and minimizing risks. Decisions here tend to be systematic and data-driven, ensuring stability and smooth daily operations. A production manager in a manufacturing company in the Philippines, for example, might concentrate on streamlining workflows to reduce costs.
Balancing these approaches allows businesses to maintain stability while evolving through innovation—ensuring long-term success.

3. Entrepreneurial Education and Training: The Foundation for Success
Entrepreneurial education represents a vital investment in developing capable, confident business leaders who can navigate challenges and seize opportunities.
Core Components of Entrepreneurial Education
Skills Development
Training programs focus on practical skills such as opportunity recognition, financial literacy, marketing, negotiation, leadership, and problem-solving. For Filipino youth, programs like the DTI’s Kapatid Mentor ME program provide hands-on learning experiences that reinforce these skills.
Practical Training
Alongside theoretical learning, aspiring entrepreneurs benefit from guidance on important steps such as business registration, securing permits and licenses, sourcing capital, and project management. This ensures they are well-prepared for real-world challenges.
Ongoing Support
Start-up phases can be difficult, requiring continued mentorship, access to networks, and resources. Incubators and accelerators in the Philippines, such as QBO Innovation Hub, offer this sustained support to help entrepreneurs refine their business models and scale up.
By incorporating these educational elements, entrepreneurial training empowers students not only to launch ventures but also to build resilient, adaptable businesses.
Local Context Application for Filipino Entrepreneurs [ Entrepreneurial Processes, Distinctions, Educational Foundations ]
Unique local factors, including cultural values, regulatory frameworks, and market conditions, shape the entrepreneurial journey in the Philippines. Community-based enterprises, such as Habi Footwear in Iloilo, combine social entrepreneurship with local craftsmanship, showcasing how strong entrepreneurial processes and education can foster a meaningful impact.
Participation in government initiatives and collaborations with NGOs focused on micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) further exemplify the importance of resource gathering and organizational formation stages.
Aspiring entrepreneurs must leverage available training programs, government grants, and mentorship opportunities tailored for Filipino contexts to increase their ventures’ chances of success.
Conclusion [ Entrepreneurial Processes, Distinctions, Educational Foundations ]
For entrepreneurship students, mastering the entrepreneurial process, differentiating it from managerial roles, and engaging in comprehensive entrepreneurial education are indispensable steps. These principles and practical insights provide a solid foundation to innovate, manage risks, and grow successful businesses, particularly within the dynamic Philippine economic environment.

References
- Kauffman Foundation: The Entrepreneurial Process
- U.S. Small Business Administration: Plan Your Business
- Department of Trade and Industry Philippines
- QBO Innovation Hub Philippines
- World Economic Forum: Managerial versus Entrepreneurial Decisions
- Asian Development Bank: Entrepreneurship in the Philippines
More Stories
- Go Hotels Plus Leads: Bacolod’s Budget Travel Elevated
- Cebu Pacific and UNICEF | 9 Years of Change for Good Campaign
- NUSTAR Sets New Standards for Luxury & Lifestyle in the Visayas
- Negros Power Bill Deposit Policy for Consumers
- Cebu Pacific’s 8.8 Seat Sale: Fly for as Low as PHP 8
- Multi-Channel Campaign Planning & Media Relations
- Innovation Through Design Thinking
- Opportunities and Challenges of Entrepreneurship | Global World
- Talisay Coastal Cleanup | Negros Power Ignites Hope and Action
- Typhoon Crising: Negros Power’s Emergency Response
- Strategic Content Creation & Storytelling
- Starting a New Business: A Practical Guide for Beginners
- Foundations of Innovation Management
- Digital Marketing, Public Relations | The Fundamentals












