Foundations of Innovation Management
Table of Contents
Foundations of Innovation Management
-
Defining Innovation and Its Types (Incremental, Radical, Disruptive)
Innovation is the process of developing new ideas, products, services, or methods that create value or solve problems in unique ways. It is a driving force behind economic growth, competitiveness, and organizational success.
Different Types of Innovation
Innovation comes in many forms, each playing a unique role in driving growth, competitiveness, and societal progress. Understanding these types helps businesses and entrepreneurs focus their efforts strategically. Below is a comprehensive list of innovation types, along with their definitions and examples.
1. Incremental Innovation
Minor, continuous improvements to existing products, services, or processes.
Example: Annual smartphone upgrades often introduce new features, such as improved cameras or faster processors.
2. Radical Innovation
Fundamental breakthroughs that create new markets or disrupt existing ones.
Example: The invention of the internet or electric cars.
3. Disruptive Innovation
Innovations that initially target niche or underserved markets and eventually displace established players.
Example: Netflix streaming is disrupting traditional video rental stores.
4. Architectural Innovation
Reconfiguring existing technologies or components to create new applications or markets without changing core technologies.
Example: Transition from desktop to laptop computers.
5. Process Innovation
New or improved methods in how products or services are created and delivered, often improving efficiency or reducing costs.
Example: Toyota’s Just-In-Time manufacturing system.
6. Product Innovation
Development of new or significantly improved goods or services that offer new features or benefits.
Example: Introduction of electric scooters for urban transport.
7. Business Model Innovation
Changing the way a company creates, delivers, and captures value, often disrupting traditional industry models.
Example: Subscription-based streaming services are replacing traditional cable TV.
8. Marketing Innovation
New marketing strategies or approaches that improve customer engagement or market reach.
Example: Influencer marketing campaigns on social media platforms.
9. Organizational Innovation
Changes in business practices, workplace organization, or external relations that improve performance.
Example: Remote work policies enabling flexible employee arrangements.
Innovations aimed at addressing social needs or problems, improving well-being, or community outcomes.
Example: Microfinance programs provide small loans to underserved entrepreneurs.

Summary Table
| Innovation Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Incremental | Minor improvements to existing offerings | Smartphone feature updates |
| Radical | Breakthroughs creating new markets | Internet invention |
| Disruptive | Innovations that disrupt existing markets | Netflix streaming |
| Architectural | Reconfiguring existing tech for new uses | Laptop computers |
| Process | New or improved production/delivery methods | Toyota Just-In-Time |
| Product | New or enhanced products/services | Electric scooters |
| Business Model | New ways to create/deliver/capture value | Subscription streaming |
| Marketing | New marketing strategies | Influencer marketing |
| Organizational | Changes in business practices or structure | Remote work policies |
| Social | Innovations addressing social challenges | Microfinance |

The Need to Innovate
Innovation is not just an option—it is a necessity for survival and growth in today’s rapidly changing world. Organizations and individuals must innovate to:
- Stay Competitive:
Markets and technologies evolve quickly. Businesses that fail to innovate risk being left behind by more agile and creative competitors. - Meet Changing Customer Needs:
Consumer preferences and expectations are constantly shifting. Innovation helps organizations respond to these changes and deliver greater value. - Drive Growth and Efficiency:
New ideas and improved processes can unlock new markets, boost productivity, and lower costs, ultimately driving sustainable growth. - Adapt to Disruption:
With the rise of digital technology and globalization, industries can be disrupted overnight. Continuous innovation ensures resilience and adaptability. - Solve Pressing Problems:
Innovation is essential for addressing complex challenges—such as environmental issues, health crises, and social inequalities—by finding new and practical solutions.

-
Overview of Product Management and Its Role in Innovation | Foundations of Innovation Management
Product Management is the practice of overseeing a product’s life cycle—from ideation and development to launch and beyond. Product managers act as the bridge between customer needs, business goals, and technical feasibility.
Key Roles in Innovation:
- Vision & Strategy: Setting the direction for new products based on market needs and opportunities.
- Cross-Functional Leadership: Coordinating among design, engineering, marketing, and sales teams.
- Lifecycle Management: Ensuring the product evolves to meet changing customer demands and stays competitive.
Example:
A product manager at a tech startup leads the development of a new app, collaborating with developers to ensure it addresses a genuine user need and stands out in the app store.

- The Entrepreneurial Mindset and Innovation Ecosystems
An entrepreneurial mindset is a way of thinking that embodies creativity, risk-taking, resilience, and adaptability. Entrepreneurs are opportunity-seekers who are not afraid to learn from failure.
Key Traits:
- Opportunity Recognition: Spotting market gaps or unmet needs.
- Resilience: Bouncing back from setbacks and persisting through challenges.
- Resourcefulness: Making the most of limited resources.
- An innovation ecosystem refers to the network of organizations, people, resources, and policies that support innovation.
Example:
Silicon Valley is an innovation ecosystem, comprising startups, investors, universities, and major tech companies that collectively foster a culture of innovation.

-
Introduction to the Design Thinking Framework | Foundations of Innovation Management
Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that focuses on understanding users, redefining problems, and creating effective solutions through iterative prototyping and testing.
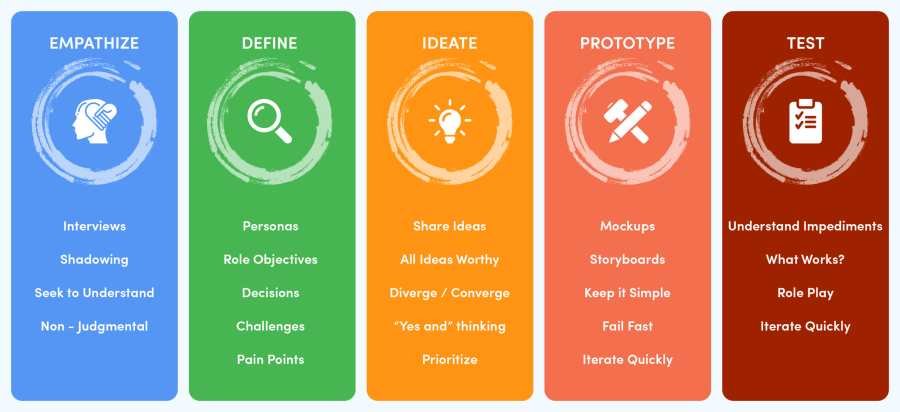
The Design Thinking Process:
- Empathize:
Understand the users and their needs through observation, interviews, and immersion.
Example: Conducting interviews with gym-goers to determine what frustrates them about current fitness apps. - Define:
Clearly articulate the user’s problem based on insights from the empathize stage.
Example: “Users find it difficult to track their workout progress efficiently.” - Ideate:
Generate a wide range of creative solutions through brainstorming and mind mapping.
Example: Brainstorming new app features like voice-activated workout logs or social sharing. - Prototype:
Build simple, inexpensive models or mock-ups of the best ideas.
Example: Creating a clickable wireframe of the new fitness app interface. - Test:
Share prototypes with real users, gather feedback, and refine the solution.
Example: Letting users try the app prototype and collecting their suggestions for improvement.
Key Terms:
- Human-centered: Focusing on the real needs and experiences of users.
- Iterative: Repeating steps, improving the solution with each cycle.

Summary Table
| Subtopic | Key Concepts & Examples |
| Types of Innovation | Incremental (smartphone updates), Radical (internet), Disruptive (Netflix) |
| Product Management | Vision, cross-functional teams, lifecycle (app development) |
| Entrepreneurial Mindset & Ecosystems | Opportunity recognition, resilience (Silicon Valley) |
| Design Thinking Process | Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, Test (fitness app example) |

References
- What is Innovation? – Harvard Business Review
- Product Management Explained – ProductPlan
- The Entrepreneurial Mindset – MIT Sloan
- Innovation Ecosystems – OECD
- What is Design Thinking? – IDEO U

More Stories
- Digital Marketing, Public Relations | The Fundamentals
- Anti-Pilferage Drive | Negros Power Slashes System Losses
- Personal Power: Stabbed but Still Slaying
- Mister Supranational 2025: France Triumphs, Philippines is 4th RU
- Transformative Trainings For Victoria’s Scholars | Two Seminars, One Mission
- Miss Supranational 2025 | Philippines Placed 3rd Runner – UP
- Tara Valencia for Miss Supranational 2025
- Smart Laundry Upgrade: Sharp Washer and Heat Pump Dryer
- Negros Power’s Major Upgrade of Bacolod-Silay 69kV Line
- Feelingera and Feelingero
- 1,671 Remote Homes Lighted in Central Negros | Negros Power











