Table of Contents
An Introduction to E-Commerce: Concepts, Skills, Business Readiness, and Modern Applications
E-commerce—short for electronic commerce—refers to the exchange of goods, services, and information through digital platforms. It is one of the most transformative developments in modern business, reshaping how consumers shop, how companies operate, and how marketing strategies are designed.
This article serves as an introductory yet expansive reference for marketing students. It explains key concepts, defines essential terms, outlines necessary skills, and presents real-world examples from major brands to illustrate how e-commerce works in practice.

Understanding E-Commerce: Concepts and Definitions
To understand e-commerce thoroughly, students need to become familiar with several foundational terms and theories.
1. E-Commerce
Definition: the buying, selling, and exchange of goods, services, and data via the internet or digital systems.
Example:
Buying a product on Amazon, booking a ride on Grab, or subscribing to Netflix are all forms of e-commerce.
2. E-Business
Definition: refers to all digital business activities—not just sales. It includes online marketing, customer service, supply chain management, and internal operations conducted electronically.
Difference vs. E-Commerce:
- E-commerce = selling and transactions
- E-business = entire digital business ecosystem
Example:
Walmart uses digital systems for inventory management, logistics automation, and customer data analytics—these are e-business processes.
3. Digital Marketplace
A platform where multiple sellers offer products/services to consumers.
Examples:
- Shopee and Lazada (Southeast Asia)
- Amazon (global)
- Alibaba (B2B wholesale)
4. M-Commerce (Mobile Commerce)
Transactions conducted via mobile devices (phones/tablets).
Example:
Purchasing food on Foodpanda or buying clothes via the Zara mobile app.
5. Omni-channel Retailing
A unified customer experience across online and offline channels.
Example:
IKEA lets customers browse online, check inventory, order for delivery, or pick up in-store—all synchronized.
6. Customer Experience (CX)
The overall feeling customers have during their interaction with a digital brand, from discovery to purchase to after-sales.
CX includes:
- Website speed
- Navigation
- Customer support
- Return and refund experience
A strong CX leads to loyalty and repeat purchases.
7. Conversion Rate
The percentage of website visitors who complete a desired action (purchase, sign-up, download).
Example:
If 100 people visit the Nike website and 3 buy shoes, the conversion rate is 3%.
Core Components of an E-Commerce System
Understanding these elements helps marketing students see the “big picture” of how online businesses operate.
1. Digital Storefront
The website or app where customers view products.
Key components:
- Product images
- Descriptions
- Reviews
- Pricing
- Search and filtering
Example:
Apple.com uses clean design and high-quality images to showcase products.
2. Payment Systems
Digital tools that allow secure transactions.
Examples:
- Digital wallets: GCash, PayPal, Apple Pay
- Credit/debit card processing
- Buy Now Pay Later: Klarna, Afterpay
3. Logistics and Fulfillment
The behind-the-scenes operations that deliver orders.
Key processes:
- Inventory management
- Warehousing
- Order picking and packing
- Shipping
- Return handling
Example:
Amazon Prime offers 1-day delivery because of its advanced fulfillment centers and robotics.
4. Digital Marketing
Strategies to attract and convert online customers.
Major techniques:
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
- Social media marketing
- Paid digital ads
- Influencer marketing
- Email campaigns
- Content creation
Example:
Coca-Cola uses social media campaigns and emotional storytelling to build engagement.
5. Analytics and Insights
Data guides decisions in e-commerce.
Metrics include:
- Click-through rate (CTR)
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
- Return on advertising spend (ROAS)
- Lifetime value (LTV)
Example:
Spotify uses user data to personalize playlists and recommend content.
6. Technology Infrastructure
E-commerce requires strong digital foundations:
- Website hosting
- Data security
- Chatbots
- API integrations
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems
Why E-Commerce Is Essential for Marketing Students and Businesses
This web-based business is no longer optional. It is a core competency for all modern marketers and an essential business capability.
1. Consumers Are Primarily Online
People research products on Google, watch reviews on TikTok, and compare prices online before buying.
2. Business Growth Depends on Digital Access
It enables even small businesses to reach global customers.
Example:
A small Filipino crafts seller can ship internationally through Etsy or Shopify.
3. Marketing Has Become Data-Driven
It provides measurable data at every stage of the customer journey.
4. Digital Sales Are Growing Every Year
Many traditional companies now generate more revenue online than in-store.
Example:
Nike Direct (its online business) has become one of the company’s fastest-growing segments.
Skills Needed to Master E-Commerce
Below are the essential skills for students who want to succeed in the web-based field:
1. Digital Marketing Competence
- SEO
- Social media strategy
- PPC ads
- Influencer partnerships
- Email marketing automation
2. Data & Analytics Literacy
Students must understand:
- Google Analytics
- Social media insights
- Conversion tracking
- Customer segmentation
3. Technical Familiarity
- Website builders (Shopify, WooCommerce)
- Basic UX/UI principles
- Understanding how product pages, carts, and checkouts work
4. Creativity & Content Production
- Product photography
- Graphic design
- Copywriting
- Brand storytelling
Example:
Glossier used user-generated content to grow its brand.
5. Customer Relationship Management
- Handling customer inquiries
- Managing reviews
- Creating loyalty programs
6. Operations & Supply Chain Awareness
Understanding inventory flow, packaging, and shipping options.
This page was hacked and is no longer the official page of Jojo Vito Designs Gallery
What Companies Must Prepare to Succeed in E-Commerce
Businesses need structural readiness—not just a website.
1. Strong Digital Infrastructure
- Fast, mobile-friendly site
- Secure payment options
- Simple checkout
2. Trained E-Commerce Team
Personnel in marketing, logistics, IT, and customer service must understand digital operations.
3. Reliable Logistics Partners
- Couriers
- Warehousing
- Inventory accuracy
4. Marketing and Branding Strategy
Consistent messaging, strong visuals, and active digital presence.
5. Cybersecurity & Privacy Compliance
Protecting customer data is mandatory.
Conclusion
E-commerce is a dynamic, multidimensional field that blends marketing strategy, digital technology, consumer psychology, and business operations. For marketing students, mastering e-commerce provides a powerful foundation for future careers. For businesses, readiness in digital systems, logistics, marketing, and analytics is essential for long-term success.

| References | Link / How to access |
|---|---|
| OECD – “E-commerce in the time of COVID-19” | https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/2020/10/e-commerce-in-the-time-of-covid-19_bb699f3a.html OECD |
| UNCTAD – “E-commerce and the digital economy” (overview) | https://unctad.org/topic/ecommerce-and-digital-economy UN Trade and Development (UNCTAD)+1 |
| IBM – (definition & explanation) | https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ecommerce IBM |
| McKinsey & Company – explainer article | https://upgrade.mckinsey.com.br/featured-insights/mckinsey-explainers/what-is-e-commerce upgrade.mckinsey.com.br |
| Statista – “E-commerce worldwide – statistics & facts” | https://www.statista.com/topics/871/online-shopping/ Statista |
| International Monetary Fund (IMF) – “E-commerce During Covid: Stylized Facts from 47 Economies” | https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WP/Issues/2022/01/28/E-commerce-During-Covid-Stylized-Facts-from-47-Economies-512014 IMF |
More Stories
- 20 TOP SINGAPORE TOURIST SPOTS | THINGS TO DO
- 24 THINGS TO DO IN CHIANG MAI | TOURIST SPOTS
- 25 THINGS TO DO IN CAMBODIA | TOURIST SPOTS
- THINGS TO DO IN TOKYO | TOURIST SPOTS
- CREMATION, A CHOICE FOR MANY FILIPINOS | Teresa Development Corporation
- 10 MEN’S FASHION HACKS | DRESS TO IMPRESS
- FOOD PRESENTATION IDEAS | THAILAND
- Sanctuary of Truth, Pattaya : Unveiling the Majestic Marvel
- Khao Yai Art Museum: Embracing the Fabulous Asian Lifestyle
- Chao Phraya Abhaibhubejhr Hospital and Thai Traditional Medicine Museum
- SSS Pensions: A Wake-Up Call for Young Filipino Employees
- Growing Old Alone in the Philippines Feels Terrifying
- Verbena, Trash, Failed Projects — and the Urgent Call for Accountability
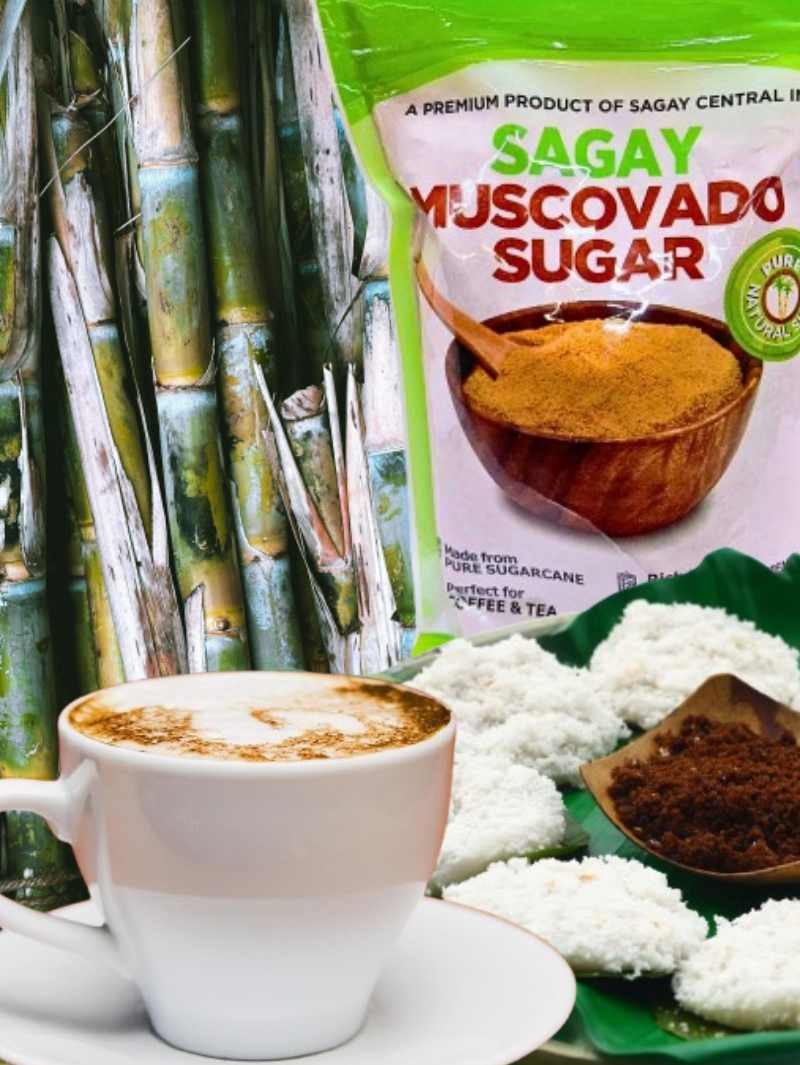















As a negrense base on my opinion and research about the Position Sagay Muscovado Sugar as a Major, all natural heritage-crafted sweetener from negros that offers richer flavor and healthier value than refined sugars. and also its authentic and artisanal production, natural wellness benefits, and deep molasses flavor to appeal to both local pride and global speciality markets. In e-commerce, market these through concise origin story, health focused infographics, and taste forward product visuals. Support this with creator partnerships.
As a negrense marketer ,I would position SAGAY MUSCOVADO SUGAR as a premium ,natural and culturally rooted sweetener that appeals to both local and international markets. To boost its global competitiveness ,I would highlight three standout aspects, First one is all natural and less processed making it healthier alternative to refined sugar. This can be market online by using simple infographics, health focused keywords, and clear product descriptions that emphasize its natural minerals and chemical free production. Second, SAGAY MUSCOVADO carries authentic negrense heritage, since it is made through traditional methods passed down through generations. In e-commerce this can be promoted by sharing farmer stories , behind the scene videos and proudly negrense branding to connect emotionally with costumers. Last is it offers a distinct premium flavor, with its deep caramel taste perfect for coffee, pastries and gourmet recipes. This can be highlighted online through high quality photos, recipe content and collaborations with food influencers. By focusing on these three points health , heritage and flavors. sagay muscovado can stand out as a unique Filipino product with strong appeal worldwide.